Using Multi-source Big Data to Explore Internal Urban Spatial Structure:
It’s one of the most important issues that how to deal with the spatial distribution of urban elements. In recent years, "big data" has brought more raw materials to urban research, while, the artificial intelligence approach has built a new platform for the diagnosis of urban spatial features based on big data.
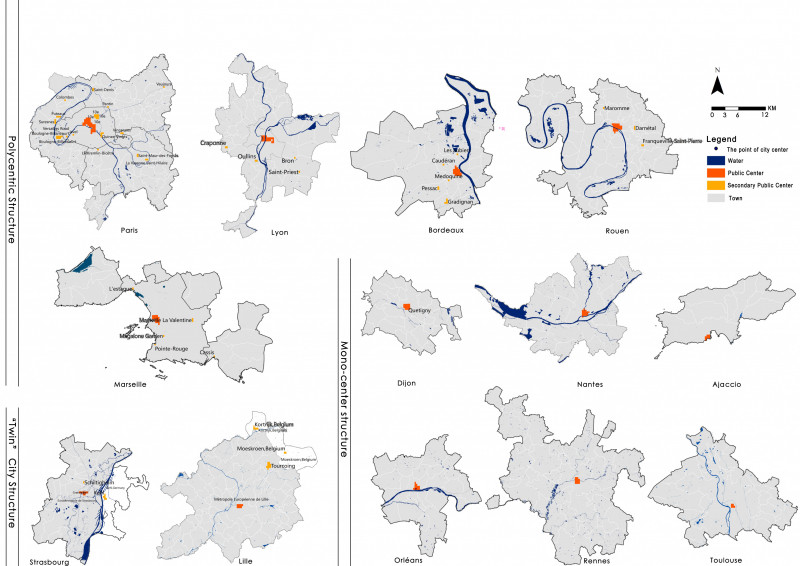
This paper defined what is the “internal urban spatial structure” at first, which is the spatial distribution characteristics of various urban elements and the interactive relationships among them. In recent decades, the classical urban spatial structure theories have experienced a change from a monocentric model to concerning polycentric phenomenon, and the explanatory variables have gradually evolved from a single element to a composite. However, production, living and public services are still the three main types of research elements, while the transportation system is the medium carrying the force among them. The easy access to multi-source big data and the increasingly convenient artificial intelligence analysis tools make it possible to explore urban spatial structure features in the full-element, full-time, and full-sample way.
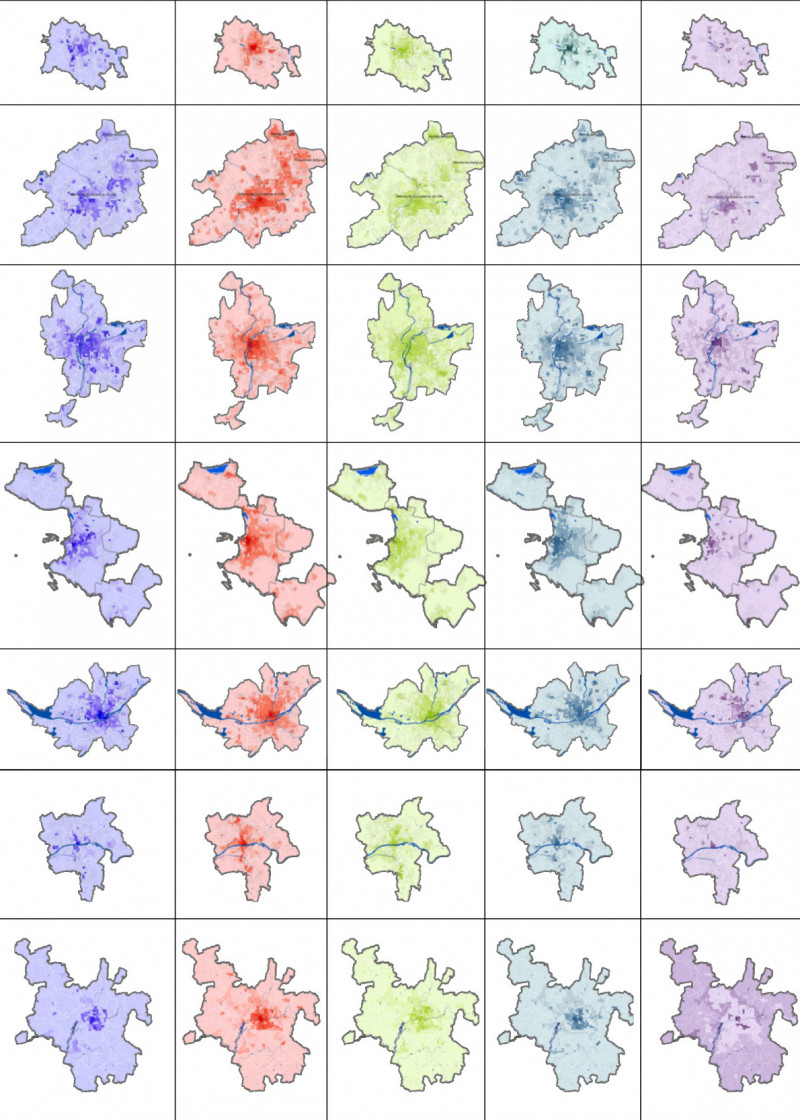
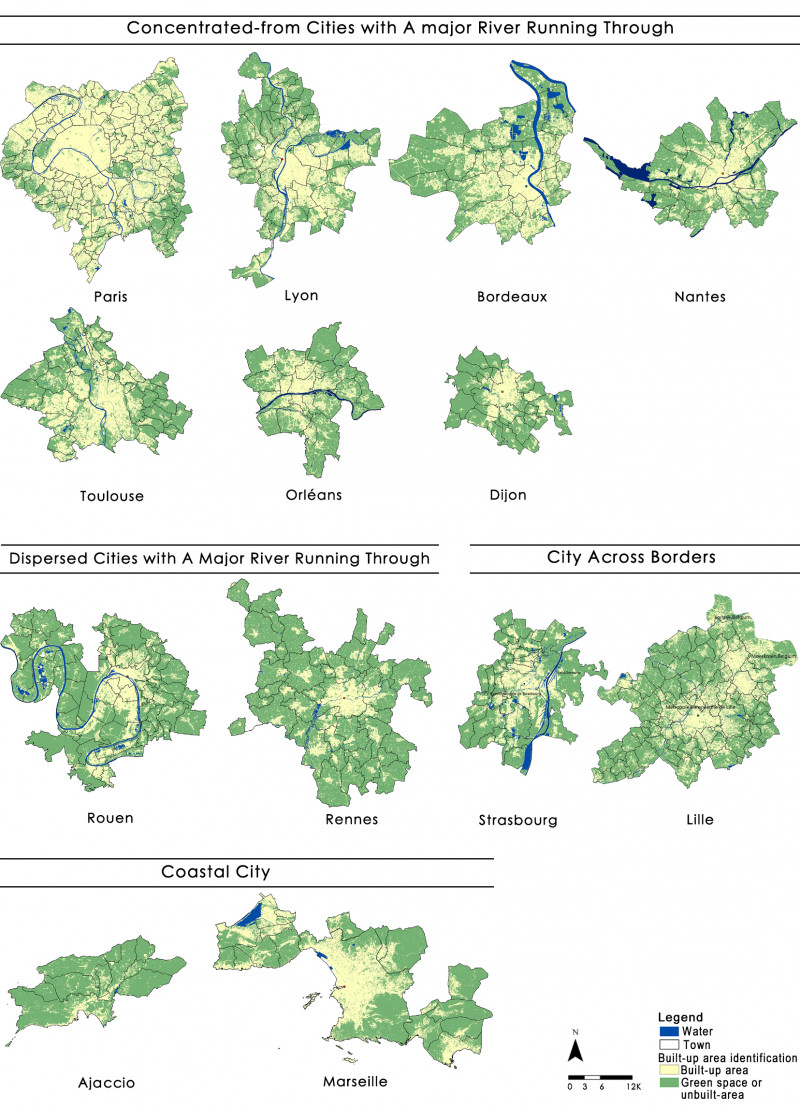
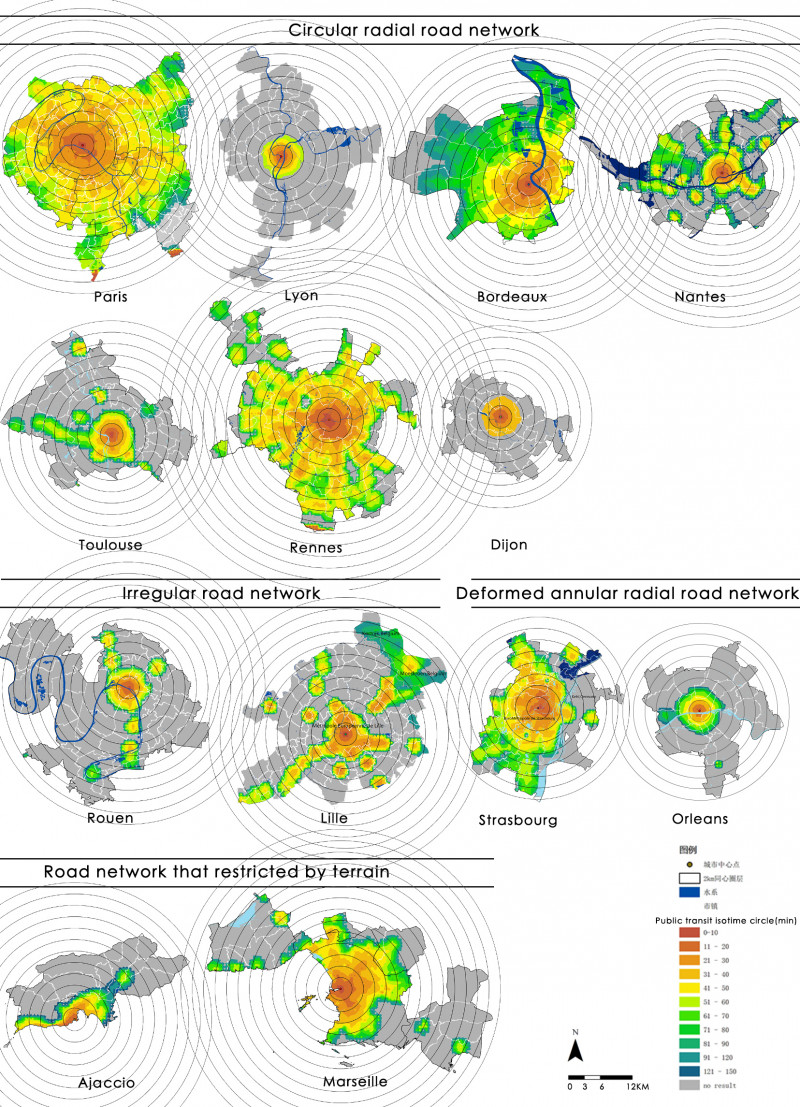
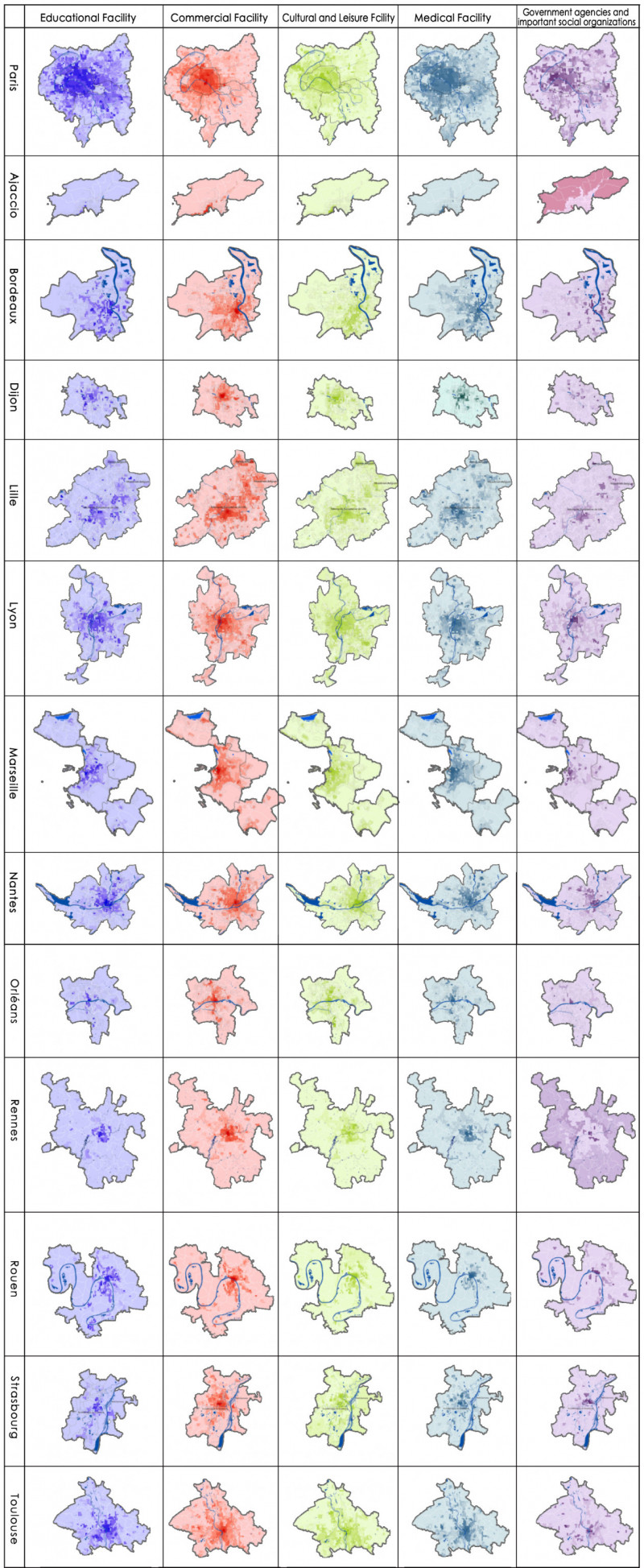
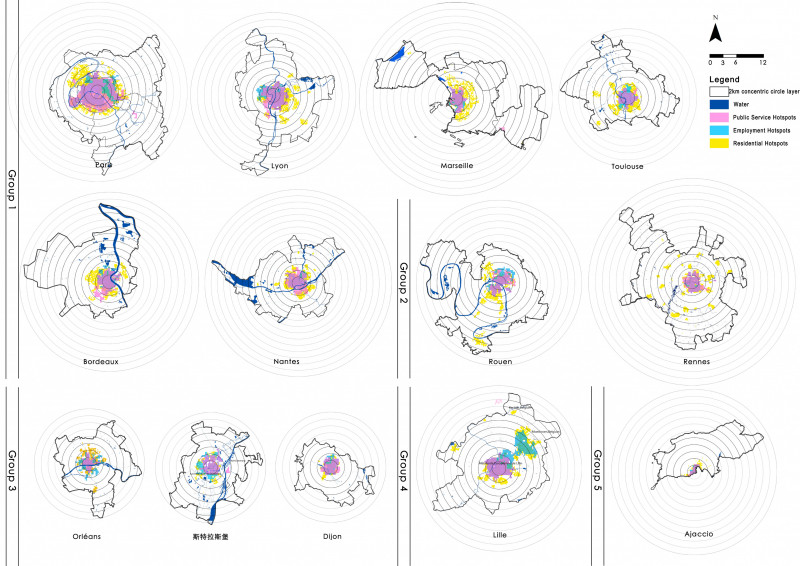
This paper selected the capitals of 13 regions in France as the research object, and divided the statistical unit through night light imagery. The remote sensing data was used to identify and judge the macroscopic urban form. The transport system, the skeleton of urban spatial structure, was analyzed by the road network and Google Map real-time traffic data. Multi-source POI were used to measure the circle structure, density distribution characteristics and multi-center structure of urban public service, employment activities and residential activities. Furthermore, the spatial distribution patterns of various urban elements, the specific ways of aggregation and the characteristics of mixed layout were further analyzed. At last, this paper analyzed the interactive relationships among different urban element by the correlation analysis and hierarchical clustering. It’s verified that the interpretive theory of classical models is reliable. And this paper explored the regularity characteristics of urban elements spatial distribution and the interactive relationships among them.
This paper provided an idea for the empirical study of urban spatial structure. And it had a deeper interpretation of the major cities in France. It was also an attempt at multi-source big data analysis.